Stream ciphers
Stream ciphers are an approximation of one-time pads. RC4 is the most well-known stream cipher, but on the edge of being insecure now.
General
Wikipedia - Stream cipher
CRYPTANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF SYNCHRONOUS STREAM CIPHERS
Hash Functions and Block Ciphers
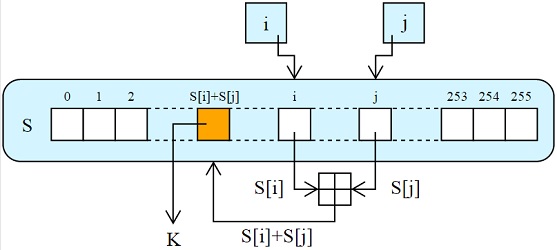
RC4
RC4 is the official algorithm, designed by Ron Rivest in 1987. It was initially a trade secret, but an anonymous poster publishe a description of it to the Cipherpunks mailing list. The algorithm derived from that description was known as ARC4, for “Alleged RC4” (because RC4 was registered as a trademark by RSA). RC4 was historically widely used in TLS, although now prohibited as of RFC 7465.
Wikipedia - RC4
Spritz
Spritz is a 2014 upgrade of RC4 by Rivest and Schuldt.
Spritz: A New RC4-Like Stream Cipher
Spritz—a spongy RC4-like stream cipher and hash function
Salsa20
Salsa20 was designed by Daniel J. Bernstein.
Wikipedia - Salsa20
ChaCha20
ChaCha20, closely related to Salsa20, was also designed by Daniel J. Bernstein, and might be slightly more secure than Salsa20. Google is now using this for Android.
Google Swaps Out Crypto Ciphers in OpenSSL
ChaCha20 and Poly1305 for IETF protocols
SOSEMANUK
Wikipedia - SOSEMANUK
Sosemanuk, a fast software-oriented stream cipher
ISAAC
Designed by Robert Jenkins (“burtlebob”) in 1996, and used in a handful of places, including inside GNU Coreutils.
Wikipedia - ISAAC
ISAAC: a fast cryptographic random number generator
Phelix
Designed by Doug Whiting, Bruce Schneier, Stefan Lucks, and Frédéric Muller.
Wikipedia - Phelix
Helix: Fast Encryption and Authentication in a Single Cryptographic Primitive
Solitaire
Designed by Bruce Schneier for Neal Stephenson to use in the book Cryptonomicon.
Wikipedia - Solitaire
One-time pads
This is the gold standard, but hard to use in practice, except in specific use cases.